Preprocessing of diffusion images
The preprocessing stage aims at correcting the non idealities affecting the diffusion data before computing the diffusion metrics. With the exception of skull stripping, all processing steps are optional and can be applied at the user discretion.
To preproccess the dMRI data, the following line of code is used. However, this results in the default preprocessing that encompass only the skull striping step. To perform more advanced preprocessing, we need to dive into the arguments of the preproc function.
study.preproc()
The arguments of the preproc function are given in the API. In this page, only the main arguments are explained in order to grasp the key aspects of preprocessing using ElikoPy.
Reslice
Description
If the raw data is not in its ’native’ resolution, a reslicing process might be required. Usually, the MRI scanner performs automatic interpolation on the data in order to beautify the data since clinicians usually have a preference for high resolution images. However, the intrinsic resolution is not augmented by this interpolation. While somewhat useful to clinicians, the interpolation is usually not desirable for research. Using it means more computation time and uncorrelated noise becoming correlated which reduces the performances of MPPCA denoising algorithms. Moreover, interpolation is not desirable when performing Gibbs ringing correction. Reslicing is therefore a way to mitigate the effect of mandatory interpolation during the acquisition.
Brain Extraction
Description
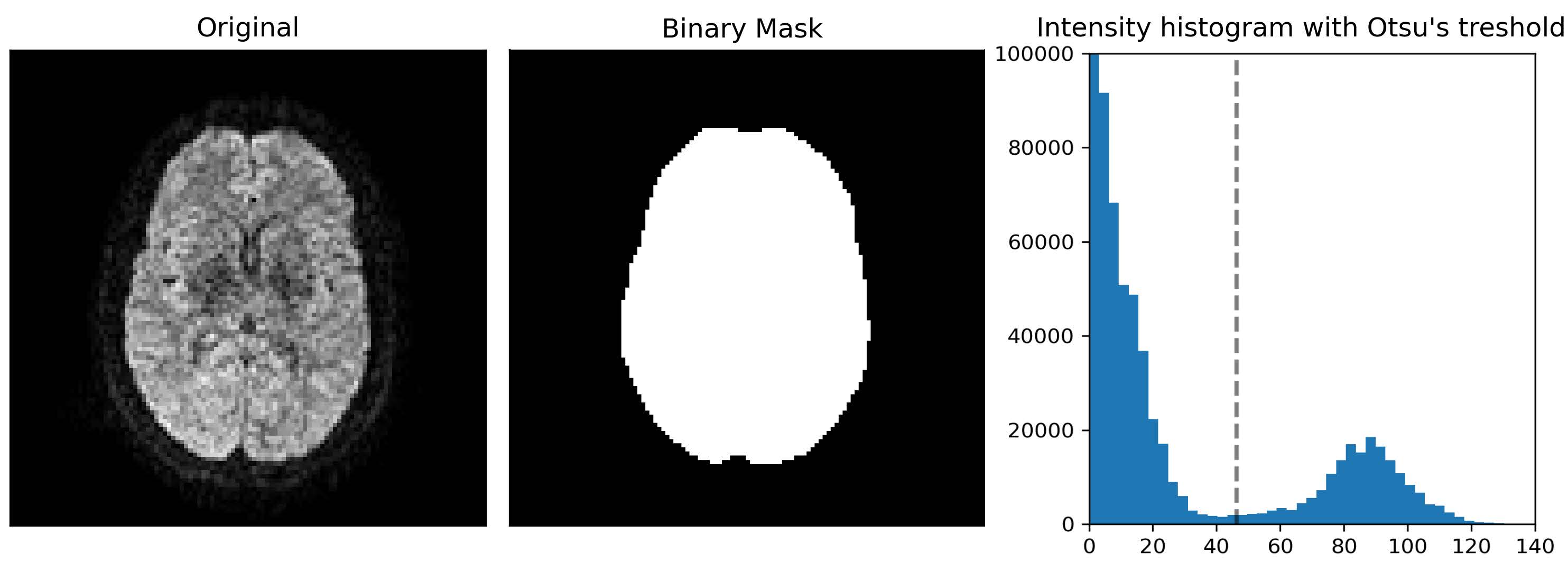
The brain is extracted from the skull and other tissues surrounding the brain to increase the processing efficiency of subsequent steps and it is generally required before using other image processing algorithms. At the end of the preprocessing, a final brain mask readjusted in regard of all the applied preprocessing steps is also provided as output.
The mask is computed using median_otsu from DiPy.

Related parameters
The brain extraction is the only mandatory step and cannot be disabled. However, it is possible to change the parameters of the method
bet_median_radius - Radius (in voxels) of the applied median filter during brain extraction. default=2
bet_numpass - Number of pass of the median filter during brain extraction. default=1
bet_dilate - Number of iterations for binary dilation during brain extraction. default=2
study.preproc(bet_median_radius=2, bet_numpass=2, bet_dilate=2)
MPPCA Denoising
Description
To reduce Rician noise typically found in MR images, the input images are denoised using the Marchenko-Pastur PCA technique as implemented in DiPy. Since the noise in diffusion data is spatially dependent in the case of multichannel receive coils, Principal component analysis of Marchenko-Pastur (MPPCA) noise-only distribution provides an accurate and fast method of noise evaluation and reduction. This methods has been chosen since it is a fast denoising algorithm that does not blur the image or create artifact.
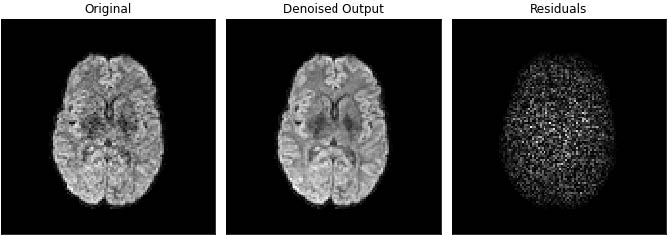
Related parameters
The denoising step during the preprocessing can be activated using the denoising argument.
study.preproc(denoising=True)
Gibbs Ringing Correction
Description
In general, in the context of diffusion-weighted imaging, derived diffusion-based estimates are affected by Gibbs oscillations. To correct for this, gibbs_removal from DiPy is used. This algorithm models the truncation of k-space as a convolution with a sinc-function in the image space. The severity of ringing artifacts thus depends on how the sampling of the sinc function occurs. The gibbs_removal function reinterpolate the image based on local, subvoxel-shifts to sample the ringing pattern at the zero-crossings of the oscillating sinc-function.
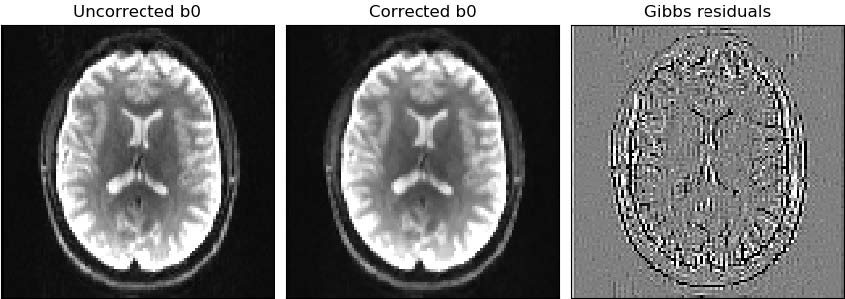
Related parameters
The Gibbs removal can be enabled using the gibbs argument.
study.preproc(gibbs=True)
Unless the data suffers heavily from Gibbs ringing artifacts, we do not advise to use the gibbs ringing removal step as it might blurr out small microstructural features.
Susceptibility field estimation
Description
Susceptibility distortions are created by differences in magnetic susceptibility near junctions of tissues. The susceptibility off resonance field is estimated using Topup from FSL. To do so, Topup needs data acquired with multiple phase encoding directions (at least 2). If only a single phase encoding direction is available, ElikoPy uses instead a generated synthetic volume based on a T1 structural image using Synb0-DisCo. This step only allows to estimate the susceptibility distortions, they are corrected at the same time as the Eddy current distortions in the Eddy step below.
Related parameters
The susceptibility field estimation can be enabled using the topup argument.
topup - true, Topup will estimate the susceptibility induced distortions. These distortions are corrected at the same time as EC-induced distortions if eddy=True. In the absence of images acquired with a reverse phase encoding direction, a T1 structural image is required. default=False
topupConfig – If not None, Topup will use additionnal parameters based on the supplied config file located at <topupConfig>. default=None
forceSynb0DisCo - If true, Topup will always estimate the susceptibility field using the T1 structural image. default=False
study.preproc(topup=True)
Note
If Topup is used, ElikoPy needs the acqparam and index files when generating the patient list : Typical usage for processing a study
Note
If topup is enabled for data with a single phase encoding direction, a T1 structural image has to be provided when generating the patient list : Typical usage for processing a study
Eddy and motion correction
Description
Motion, susceptibility and Eddy current induced distortions are artifacts with different origins but a similar effect i.e the displacement and deformation of the brain. They can therefore be jointly corrected. This is achieved using FSL Eddy. The susceptibility distortions are only corrected if they have been estimated during the topup step. By default only the inter-volume (volume-to-volume) motion is corrected but it is also possible to correct for intra-volume (slice-to-volume) motion.
Related parameters
The motion and distortion correction can be activated using the eddy argument. The number of iteration for the motion correction algorithm can also be changed.
study.preproc(eddy=True, niter=5)
In cases with large motion, inter-volume motion correction might not be sufficient and intra-volume correction is required. This option can be enabled using the s2v argument. The s2v input is a list of 4 parameters : [mporder,s2v_niter,s2v_lambda,s2v_interp]. The slice-to-volume motion correction is performed if mporder>0. These parameters are explained in depth in the Eddy FSL documentation. If N describes the number of excitations in a volume, setting mporder to N/4 while letting the other 3 parameters to their default values should provide good results in most situations. The slice-to-volume motion correction is currently only possible with cuda enabled.
Using the framework of Eddy FSL, it is also possible to replace outlier slices. This is done with the olrep argument which is a list of 4 parameters : [repol,ol_nstd,ol_nvox,ol_type]. The outlier replacement is performed if repol==True. These parameters are explained in depth in the Eddy FSL documentation.
study.preproc(eddy=True, niter=5, s2v=[6,5,1,'trilinear'], cuda=True, cuda_name='eddy_cuda10.1', olrep=[True, 4, 250, 'sw'])
Note
If Eddy FSL is used, ElikoPy needs the acqparam and index files when generating the patient list Typical usage for processing a study.
Note
If slice-to-volume motion correction is enabled, ElikoPy needs the slspec file when generating the patient list Typical usage for processing a study.
Bias Field Correction
Description
Variability of the signal in tissues of the same type can affect microstructural metrics computation and brain segmentation algorithms. This can be corrected using the N4 Bias Field Correction algorithm.
Related parameters
The bias field correction can be activated using the biasfield argument. It is also possible to modify the parameters of the correction method.
biasfield_bsplineFitting - Define the initial mesh resolution in mm and the bspline order of the biasfield correction tool.
biasfield_convergence - Define the maximum number of iteration and the convergences threshold of the biasfield correction tool.
study.preproc(biasfield=True, biasfield_bsplineFitting=[100,3], biasfield_convergence=[1000,0.001])
Report
By default, the preproc function outputs a quality report that contains quality control features for the processing. This can be disabled if needed.
study.preproc(report=False)